|
Từ điển Oxford Advanced Learner 8th
 vote
vote

vote [vote votes voted voting] noun, verb BrE [vəʊt] NAmE [voʊt]
noun
1. countable ~ (for/against sb/sth) a formal choice that you make in an election or at a meeting in order to choose sb or decide sth
• There were 21 votes for and 17 against the motion, with 2 abstentions.
• The motion was passed by 6 votes to 3.
•The chairperson has the casting/deciding vote.
•The Green candidate won over 3 000 of the 14 000 votes cast.
2. countable ~ (on sth) an occasion when a group of people vote on sth
•to have/take a vote on an issue
• The issue was put to the vote.
• The vote was unanimous.
3. the votesingular the total number of votes in an election
• She obtained 40% of the vote.
• The party increased their share of the vote.
4. the votesingular the vote given by a particular group of people, or for a particular party, etc
•the student vote
•the Labour vote
5. the votesingular the right to vote, especially in political elections
• In Britain and the US, people get the vote at 18.
see also ↑block vote
Word Origin:
late Middle English: from Latin votum ‘a vow, wish’, from vovere ‘to vow’. The verb dates from the mid 16th cent.
Culture:
elections
In Britain, a general election takes place at least every five years, when the electorate (= all the people in the country who can vote) vote for the Members of Parliament or MPs in the ↑House of Commons. Each MP represents a constituency, which is an area of the country with a roughly equal number of people (about 90 000 people) and is expected to be interested in the affairs of the constituency and to represent the interests of local people. If an MP dies or resigns, a ↑by-election is held in the constituency he or she represented. Before an election one person is chosen by each of the main political parties to be their candidate. Independent candidates, who do not belong to a political party, can also stand for election. Each candidate has to leave a deposit with the ↑returning officer, the person responsible for managing the election, which is returned to them if they win more than 5% of the votes, otherwise they lose their deposit. Before an election, candidates campaign for support in their constituency and local party workers spend their time canvassing, going from house to house to ask people about how they intend to vote. At the national level the parties spend a lot of money on advertising and media coverage. They cannot buy television time, but each party is allowed a number of strictly timed ↑party political broadcasts.
Anyone over the age of 18 has the right to vote at elections, provided they are on the electoral register (= list of adults in a constituency). Voting is not compulsory. The turnout (= number of people who vote) in recent general elections has been about 60%, although in the past 75% was more usual. On the day of the election, called polling day, voters go to a polling station, often in a local school or church hall, and are given a ballot paper. The ballot paper lists all the candidates for that constituency and the parties they represent. The voter goes into a polling booth, where nobody can see what he or she is writing, and puts a cross next to the name of one candidate only. After the polls close, the ballot papers are taken to a central place to be counted. Counting usually takes place on the same day as the election, continuing late into the night if necessary. If the number of votes for two candidates is very close, they can demand a recount. Only the candidate who gets the most votes in each constituency is elected. This system is called first past the post. The winning party, which forms the next government, is the one that wins most seats in Parliament (= has the most MPs).
In the US, elections are held regularly for President of the US, for both houses of ↑Congress and for state and local government offices. Candidates usually run for office with the support of one of the two main political parties, the Republicans or the Democrats, although anyone wanting to run as an independent can organize a petition and ask people to sign it. Some people also run as ↑write-in candidates: they ask voters to add their name to the ballot when they vote. A large amount of money is spent on election campaigning, where candidates try to achieve name recognition (= making their names widely known) by advertising on television, in newspapers and on posters. They take part in debates and hold rallies where they give speeches and go round ‘pressing the flesh’, shaking hands with as many voters as possible.
Only a person over 35 who was born in the US can run for President. Presidential elections are held every four years and early in election year, the political parties choose their candidates through a series of ↑primary elections held in each state. As these races take place it gradually becomes clear which candidates are the strongest and in the summer each party holds a convention to make the final choice of candidates for President and Vice-President. In November, the people go to vote and although the President is said to be directly elected, the official vote is made by an ↑electoral college. Each state has a certain number of electors in the college based on the state’s population. All the electors from a state must vote for the candidate who got the most votes in the state, and the candidate with at least 270 votes out of 538 becomes President. After the election, the new President goes to Washington for the inauguration on 20 January, and takes the oath of office.
Americans over the age of 18 have the right to vote, but only about half of them take part in presidential elections and voter turnout for other elections is even lower. On election day, voters go to polling stations where they first have to sign their name in a book that lists all the voters in the precinct (= area) and then cast a vote. Some states use computerized voting systems and in others voters pull down a metal lever beside the name of the person they want to vote for which operates a mechanical counter. It is possible to select all the candidates from one party, which is called voting a straight ticket, but many voters choose candidates from both parties and vote a split ticket. Journalists and pollsters are allowed to ask people how they voted and these exit polls help to predict election results. However, the results of exit polls may not be announced until polling stations everywhere have closed, in case they influence the result.
Collocations:
Politics
Power
create/form/be the leader of a political party
gain/take/win/lose/regain control of Congress
start/spark/lead/be on the brink of a revolution
be engaged/locked in an internal power struggle
lead/form a rival/breakaway faction
seize/take control of the government/power
bring down/overthrow/topple the government/president/regime
abolish/overthrow/restore the monarchy
establish/install a military dictatorship/a stable government
be forced/removed/driven from office/power
resign/step down as party leader/an MP/president/prime minister
enter/retire from/return to political life
Political debate
spark/provoke a heated/hot/intense/lively debate
engage in/participate in/contribute to (the) political/public debate (on/over sth)
get involved in/feel excluded from the political process
launch/start/lead/spearhead a campaign/movement
join/be linked with the peace/anti-war/feminist/civil rights movement
criticize/speak out against/challenge/support the government
lobby/put pressure on the government (to do sth)
come under fire/pressure from opposition parties
Policy
call for/demand/propose/push for/advocate democratic/political/land reform(s)
formulate/implement domestic economic policy
change/influence/shape/have an impact on government/economic/public policy
be consistent with/be in line with/go against/be opposed to government policy
reform/restructure/modernize the tax system
privatize/improve/deliver/make cuts in public services
invest (heavily) in/spend sth on schools/education/public services/(the) infrastructure
nationalize the banks/the oil industry
promise/propose/deliver/give ($80 billion in/significant/substantial/massive) tax cuts
a/the budget is approved/ (especially NAmE) passed by parliament/congress
Making laws
have a majority in/have seats in Parliament/Congress/the Senate
propose/sponsor a bill/legislation/a resolution
introduce/bring in/draw up/draft/adopt/pass a bill/a law/legislation/measures
amend/repeal an act/a law/legislation
veto/vote against/oppose a bill/legislation/a measure/a proposal/a resolution
get/require/be decided by a majority vote
more collocations at ↑economy, ↑voting
Collocations:
Voting in elections
Running for election
conduct/hold an election/a referendum
(especially NAmE) run for office/election/governor/mayor/president/the White House
(especially BrE) stand for election/office/Parliament/the Labour Party/a second term
hold/call/contest a general/national election
launch/run a presidential election campaign
support/back a candidate
sway/convince/persuade voters/the electorate
appeal to/attract/woo/target (NAmE) swing voters/(BrE) floating voters
fix/rig/steal an election/the vote
Voting
go to/be turned away from (especially BrE) a polling station/(NAmE) a polling place
cast a/your vote/ballot (for sb)
vote for the Conservative candidate/the Democratic party
mark/spoil your ballot paper
count (BrE) the postal votes/(especially NAmE) the absentee ballots
go to/be defeated at the ballot box
get/win/receive/lose votes
get/win (60% of) the popular/black/Hispanic/Latino/Muslim vote
win the election/(in the US) the primaries/a seat in Parliament/a majority/power
lose an election/the vote/your majority/your seat
win/come to power in a landslide (victory) (= with many more votes than any other party)
elect/re-elect sb (as) mayor/president/an MP/senator/congressman/congresswoman
Taking power
be sworn into office/in as president
take/administer (in the US) the oath of office
swear/take (in the UK) an/the oath of allegiance
give/deliver (in the US) the president's inaugural address
take/enter/hold/leave office
appoint sb (as) ambassador/governor/judge/minister
form a government/a cabinet
serve two terms as prime minister/in office
more collocations at ↑economy, ↑politics
Synonyms:
election
vote • poll • referendum • ballot
These are all words for an event in which people choose a representative or decide sth by voting.
election • an occasion on which people officially choose a political representative or government by voting: ▪ Who did you vote for in the last election?
vote • an occasion on which a group of people vote for sb/sth: ▪ They took a vote on who should go first.
poll • (journalism) the process of voting in an election: ▪ They suffered a defeat ▪ at the polls ▪.
referendum • an occasion on which all the adults in a country can vote on a particular issue
ballot • the system of voting by marking an election paper, especially in secret; an occasion on which a vote is held: ▪ The leader will be chosen by secret ballot.
Ballot is usually used about a vote within an organization rather than an occasion on which the public vote.
a national/local election/vote/poll/referendum/ballot
to have/hold/conduct a(n) election/vote/poll/referendum/ballot
Example Bank:
•A special vote of thanks went to the organizer, Tim Woodhouse.
•Any senator can force a vote on virtually any proposal.
•Bush had courted the military vote.
•Everyone's vote counts.
•Ferrer got 84% of the Hispanic vote.
•He lost the election because of the protest vote.
•He won the seat thanks to Polish block votes.
•How many years is it since women have had the vote?
•Let's take a vote on the issue.
•Members are elected by direct vote.
•Members of Parliament will have a free vote on this bill.
•Mr Olsen was approved by a vote of 51–47.
•My vote will go to the party that addresses crime.
•Our candidate polled only 10% of the vote.
•The bill was passed by a single vote.
•The chairperson always has the casting vote.
•The government received a massive vote of confidence from the electorate.
•The law was ratified by popular vote.
•The party's vote fell by 6%.
•The single transferable vote system operates.
•The union wants the system of block votes to continue.
•They want to persuade voters to change their vote.
•Votes are still being counted.
•We should put the resolution to the vote.
•We took a quick vote to decide on a leader.
•You can cast your vote at the local polling station.
•a vote for the government
•a vote on the new law
•an overwhelming vote in favour of autonomy
•factors that could swing the vote against the president
•the party that split the Republican vote
•I think it's time to put this issue to the vote.
•Let me propose a vote of thanks.
•They held a vote of no confidence in the government.
•They took a vote on who should be their new leader.
•When will we know the outcome of the vote?
Idiom: ↑vote with your feet
Derived: ↑vote somebody down ▪ ↑vote somebody in ▪ ↑vote somebody into something ▪ ↑vote somebody out ▪ ↑vote somebody out of something ▪ ↑vote something through
verb
1. intransitive, transitive to show formally by marking a paper or raising your hand which person you want to win an election, or which plan or idea you support
•~ (for/against sb/sth) Did you vote for or against her?
• How did you vote at the last election?
•~ in favour of sth Over 60% of members voted in favour of (= for) the motion.
•~ (on sth) We'll listen to the arguments on both sides and then vote on it.
•Only about half of the electorate bothered to vote.
•~ sth We voted Democrat in the last election.
•~ to do sth Parliament voted to set up an independent inquiry into the matter.
2. transitive, usually passive ~ sb/sth + noun to choose sb/sth for a position or an award by voting
• He was voted most promising new director.
3. transitive, usually passive ~ sth + noun to say that sth is good or bad
• The event was voted a great success.
4. transitive ~ sb/yourself sth to agree to give sb/yourself sth by voting
•The directors have just voted themselves a huge pay increase.
5. transitive ~ (that)… to suggest sth or support a suggestion that sb has made
•I vote (that) we go out to eat.
Verb forms: 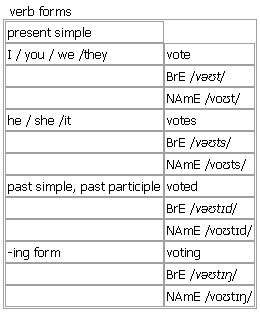
Word Origin:
late Middle English: from Latin votum ‘a vow, wish’, from vovere ‘to vow’. The verb dates from the mid 16th cent.
Collocations:
Politics
Power
create/form/be the leader of a political party
gain/take/win/lose/regain control of Congress
start/spark/lead/be on the brink of a revolution
be engaged/locked in an internal power struggle
lead/form a rival/breakaway faction
seize/take control of the government/power
bring down/overthrow/topple the government/president/regime
abolish/overthrow/restore the monarchy
establish/install a military dictatorship/a stable government
be forced/removed/driven from office/power
resign/step down as party leader/an MP/president/prime minister
enter/retire from/return to political life
Political debate
spark/provoke a heated/hot/intense/lively debate
engage in/participate in/contribute to (the) political/public debate (on/over sth)
get involved in/feel excluded from the political process
launch/start/lead/spearhead a campaign/movement
join/be linked with the peace/anti-war/feminist/civil rights movement
criticize/speak out against/challenge/support the government
lobby/put pressure on the government (to do sth)
come under fire/pressure from opposition parties
Policy
call for/demand/propose/push for/advocate democratic/political/land reform(s)
formulate/implement domestic economic policy
change/influence/shape/have an impact on government/economic/public policy
be consistent with/be in line with/go against/be opposed to government policy
reform/restructure/modernize the tax system
privatize/improve/deliver/make cuts in public services
invest (heavily) in/spend sth on schools/education/public services/(the) infrastructure
nationalize the banks/the oil industry
promise/propose/deliver/give ($80 billion in/significant/substantial/massive) tax cuts
a/the budget is approved/ (especially NAmE) passed by parliament/congress
Making laws
have a majority in/have seats in Parliament/Congress/the Senate
propose/sponsor a bill/legislation/a resolution
introduce/bring in/draw up/draft/adopt/pass a bill/a law/legislation/measures
amend/repeal an act/a law/legislation
veto/vote against/oppose a bill/legislation/a measure/a proposal/a resolution
get/require/be decided by a majority vote
more collocations at ↑economy, ↑voting
Collocations:
Voting in elections
Running for election
conduct/hold an election/a referendum
(especially NAmE) run for office/election/governor/mayor/president/the White House
(especially BrE) stand for election/office/Parliament/the Labour Party/a second term
hold/call/contest a general/national election
launch/run a presidential election campaign
support/back a candidate
sway/convince/persuade voters/the electorate
appeal to/attract/woo/target (NAmE) swing voters/(BrE) floating voters
fix/rig/steal an election/the vote
Voting
go to/be turned away from (especially BrE) a polling station/(NAmE) a polling place
cast a/your vote/ballot (for sb)
vote for the Conservative candidate/the Democratic party
mark/spoil your ballot paper
count (BrE) the postal votes/(especially NAmE) the absentee ballots
go to/be defeated at the ballot box
get/win/receive/lose votes
get/win (60% of) the popular/black/Hispanic/Latino/Muslim vote
win the election/(in the US) the primaries/a seat in Parliament/a majority/power
lose an election/the vote/your majority/your seat
win/come to power in a landslide (victory) (= with many more votes than any other party)
elect/re-elect sb (as) mayor/president/an MP/senator/congressman/congresswoman
Taking power
be sworn into office/in as president
take/administer (in the US) the oath of office
swear/take (in the UK) an/the oath of allegiance
give/deliver (in the US) the president's inaugural address
take/enter/hold/leave office
appoint sb (as) ambassador/governor/judge/minister
form a government/a cabinet
serve two terms as prime minister/in office
more collocations at ↑economy, ↑politics
Example Bank:
•Everyone over 18 has the right to vote.
•Her party voted with the government.
•Parliament is to vote on tobacco advertising tomorrow.
•She returned home in order to vote in the elections.
•She was elected on the second round of voting.
•She was voted off the committee.
•Stockholders have the right to vote on the proposal.
•The Senate voted narrowly to continue funding the plan.
•The committee voted in favour of the plan.
•The committee voted unanimously to accept the plans.
•The proposal was voted down.
•The proposals were formally voted upon.
•They all voted for the new tax.
•They voted 15 to 2 to accept the offer.
•They voted overwhelmingly against the proposal.
•They voted yes to the agreement.
•the government that has just been voted into power
•young people who are eligible to vote for the first time
•Over 60% of members voted in favour of the motion.
•Parliament voted to set up an independent enquiry into the matter.
•We'll listen to the arguments on both sides and then vote on it.
|
|
|
▼ Từ liên quan / Related words
Related search result for "vote"
|
|